THE MIZ STUDY
The Marginal Ice Zone (MIZ) Study is a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary, and collaborative Antarctic science program that focuses on one of the fastest-changing regions of the Southern Ocean.
This science project has been designed to provide samples, data, and synergistic analysis to understand the (East) Antarctic marginal ice zone (MIZ), and its efficiency in promoting (or reducing) ocean, atmosphere and ecosystem functions.
The MIZ Study will deliver essential information and material for government policy and meet international obligations, including long-term monitoring, in-situ* datasets, and Earth System analysis.
*in-situ (collected in the field during an expedition / as opposed to remotely sensed) datasets
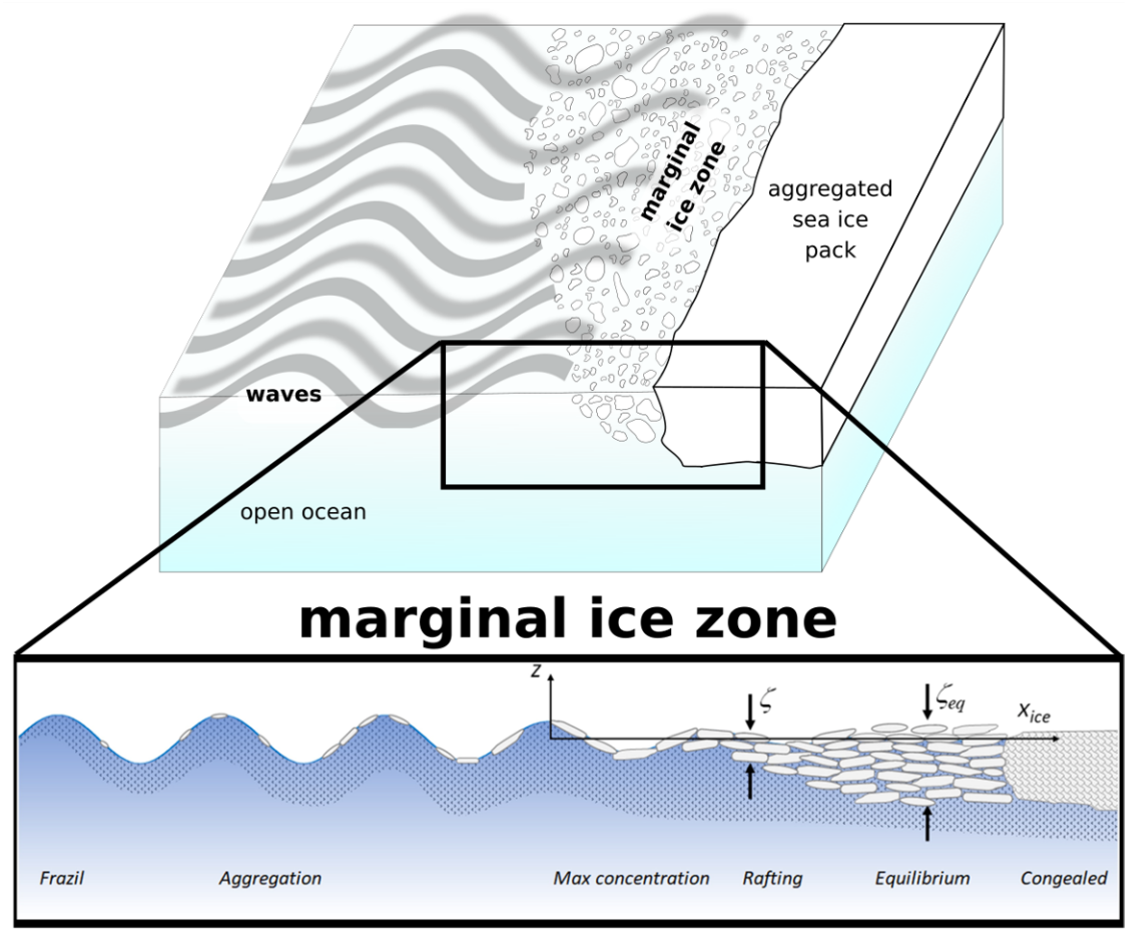
DEFINITION OF THE MIZ
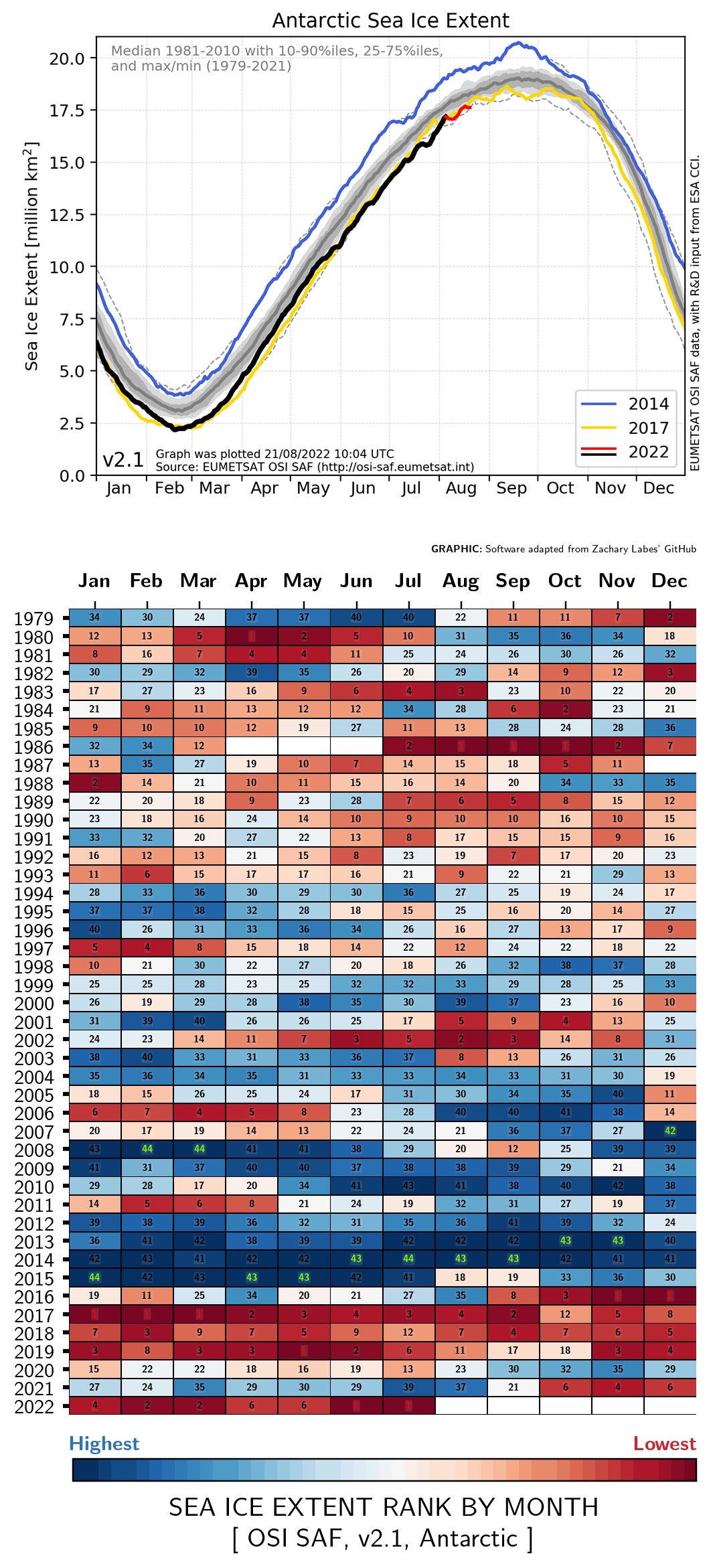
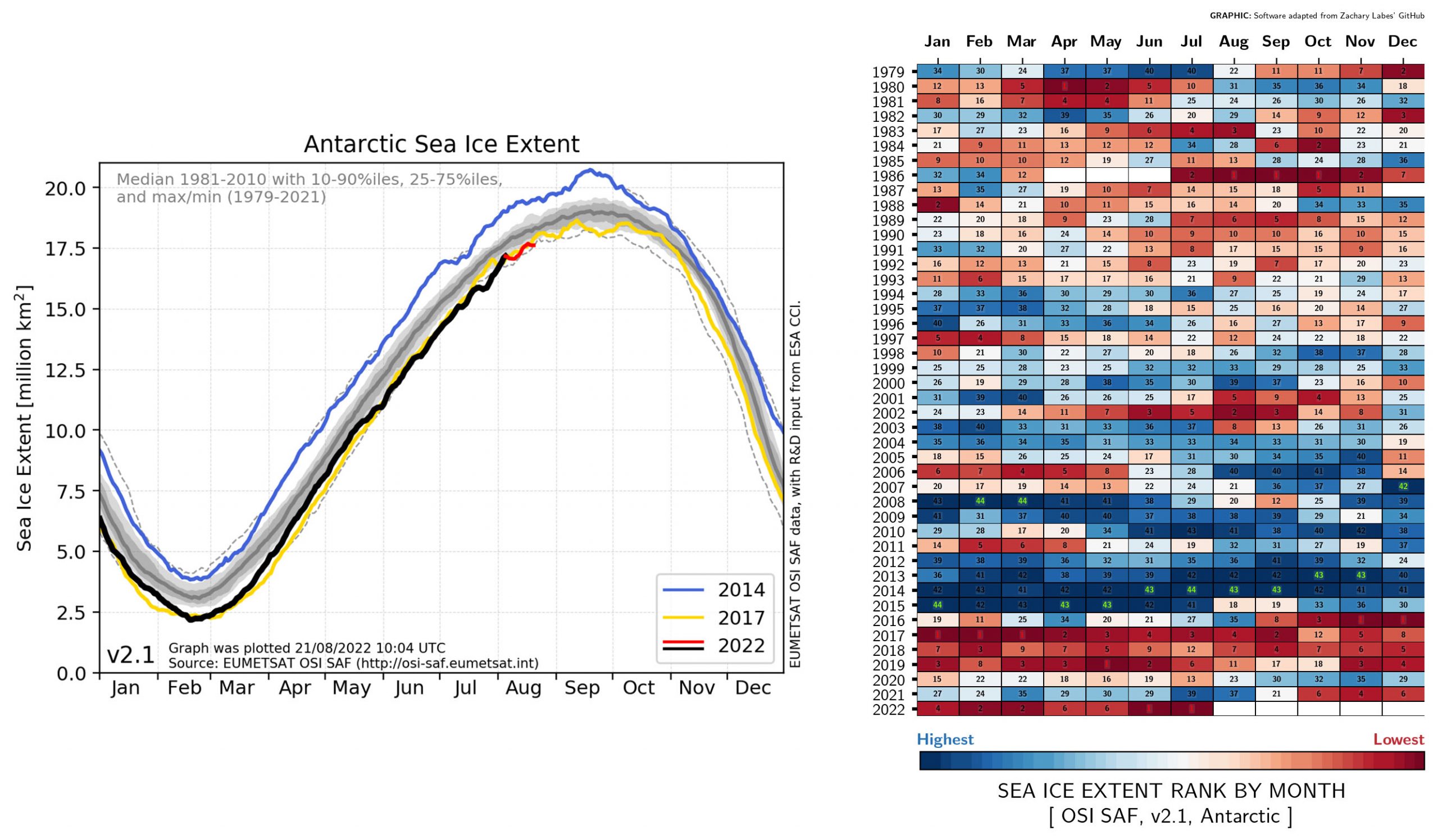
MIZ (Marginal Ice Zone) is the transition from compact sea ice to open ocean. The definition is related to both sea-ice concentration and wave effect on sea ice, usually a combination of both.